Object oriented programming concepts is generally termed as OOPs which uses Object in programming.
It uses Inheritance, polymorphism, abstraction and Encapsulation.
The main purpose of this concept is to increase the re usability and maintainability.
Let us discuss below the OOP’s concepts in detail
OOPs:
- Object
- Class
- Method
- Polymorphism
- Inheritance
- Abstraction
- Encapsulation
Object
Object is an instance of Class. It mainly contains state and behavior of a class
Vehicle is a java class which consists of state i.e., color and model
It also consist of behavior i.e., accelrateVehicle() and honkVehicle()
obj is an object for a java class Vehicle

In general all instance variables are called State of the class and methods are called behavior of the class
package com.itwhistle.oops;
public class Vehicle {
public String color;
public String model;
public void accelrateVehicle() {
System.out.println("Vehicle is accelrating now");
}
public void honkVehicle() {
System.out.println("Honk the vehicle");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// obj is an object which creates an instance of class "Vehicle"
Vehicle obj = new Vehicle();
// State of the vehicle, setting black and BMW
obj.color = "Black";
obj.model = "BMW";
System.out.println("Vehicle Color " + obj.color);
System.out.println("Vehicle Model " + obj.model);
// Behavior of vehicle
obj.accelrateVehicle();
obj.honkVehicle();
}
}
Class
Class is a blueprint or template which contains variables(state) and methods(behavior)
In the below example, we are creating two objects for same Vehicle class but the properties are different

package com.itwhistle.oops;
public class Vehicle {
public String color;
public String model;
public void accelrateVehicle() {
System.out.println("Vehicle is accelrating now");
}
public void honkVehicle() {
System.out.println("Honk the vehicle");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// obj is an object which creates an instance of class "Vehicle"
Vehicle obj1 = new Vehicle();
Vehicle obj2 = new Vehicle();
// State of the vehicle, setting black and BMW
obj1.color = "Black";
obj1.model = "BMW";
// State of the vehicle, setting White and Dodge
obj2.color = "White";
obj2.model = "Dodge";
System.out.println("Vehicle Color " + obj1.color);
System.out.println("Vehicle Model " + obj1.model);
System.out.println("Vehicle Color " + obj2.color);
System.out.println("Vehicle Model " + obj2.model);
// Behavior of vehicle
obj1.accelrateVehicle();
obj1.honkVehicle();
}
}
If you would like to learn the basics of Java syntax please click here
Method
Method consists group of statements which will get executed based upon on the caller
In the below example, a method executes with parameters and return type also it throws an exception

package com.itwhistle.oops;
public class MethodTest {
public static int add(int x, int y) throws Exception {
int z = 0;
z = x + y;
return z;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("adding two numbers "+add(5, 5));;
}
}
Polymorphism
It is an object oriented programming concepts where one to many relationship is applicable.
An object can take multiple forms is otherwise called Polymorphism
It has two types of polymorphism
- Run time polymorphism
- Compile time polymorphism
Run Time Polymorphism:
Method Overriding is famously called as Runtime(dynamic binding) polymorpshim.
Method overriding uses same method name with same parameters and return type in child class which exists in parent class with different logic inside the method.
Therefore in the below example it calls the same method “accelrateVehicle()” is written with different print statement.
In Run time it calls accelrateVehicle() from child or super class based on the object creation
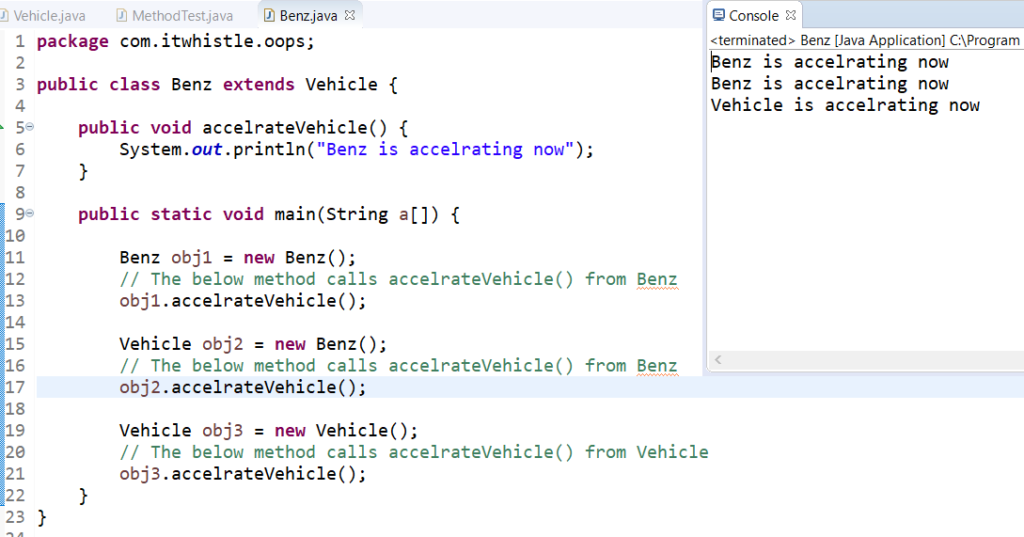
package com.itwhistle.oops;
public class Benz extends Vehicle {
public void accelrateVehicle() {
System.out.println("Benz is accelrating now");
}
public static void main(String a[]) {
Benz obj1 = new Benz();
// The below method calls accelrateVehicle() from Benz
obj1.accelrateVehicle();
Vehicle obj2 = new Benz();
// The below method calls accelrateVehicle() from Benz
obj2.accelrateVehicle();
Vehicle obj3 = new Vehicle();
// The below method calls accelrateVehicle() from Vehicle
obj3.accelrateVehicle();
}
}
Compile Time Polymorphism
Method overloading commonly called as Compile time(static binding) polymorphism.
Method overloading uses same same method name with different parameters and return type
Therefore in the below example it calls the add method based on the parameters passed, it throws an error compile time if you use same method name and same parameters
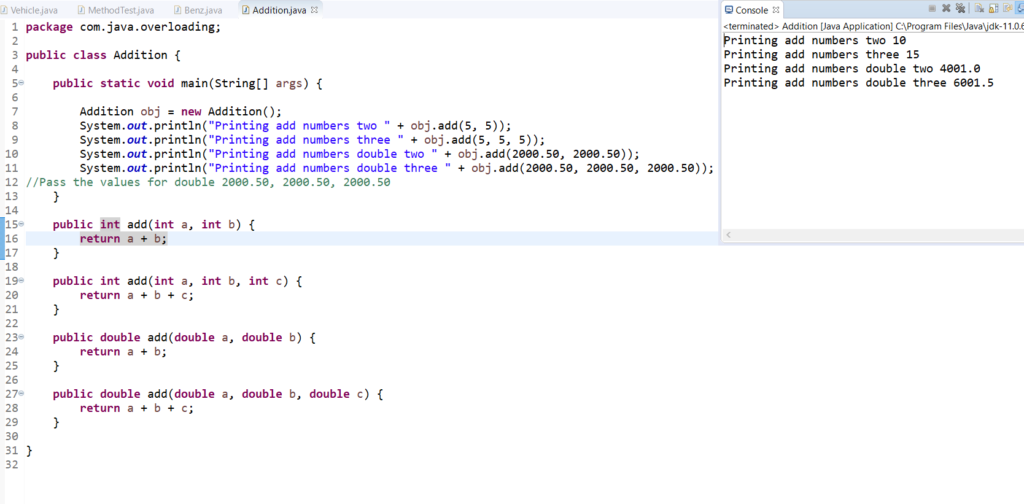
package com.java.overloading;
public class Addition {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Addition obj = new Addition();
System.out.println("Printing add numbers two " + obj.add(5, 5));
System.out.println("Printing add numbers three " + obj.add(5, 5, 5));
System.out.println("Printing add numbers double two " + obj.add(2000.50, 2000.50));
System.out.println("Printing add numbers double three " + obj.add(2000.50, 2000.50, 2000.50));
//Pass the values for double 2000.50, 2000.50, 2000.50
}
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
public int add(int a, int b, int c) {
return a + b + c;
}
public double add(double a, double b) {
return a + b;
}
public double add(double a, double b, double c) {
return a + b + c;
}
}
Inheritance
Inheritance allows you to access the super class properties into the sub class. It is mainly useful for re usability of the the java code
You need to know three things mainly, Super class, Sub class and extends(Keyword)
There are two types of inheritance:
- Single Inheritance
- Multi-Level Inheritance

Lets talk about each type separately below:
Single Inheritance
One child class extends one super class is called Single Inheritance
As you can see in the below example Dog extends Animal so it can inherit all the properties of Animal


Dog inherits the Animal property such as sleep(), drink() and walk() is Single Inheritance
package com.itwhistle.oops;
public class Animal {
public void sleep()
{
System.out.println("Animal is sleeping");
}
public void walk()
{
System.out.println("Animal is walking");
}
public void drink()
{
System.out.println("Animal is drinking");
}
}package com.itwhistle.oops;
public class Dog extends Animal{
public static void main(String a[])
{
Dog dog=new Dog();
dog.bark();
dog.eat();
dog.sleep();
dog.drink();
dog.walk();
}
public void bark()
{
System.out.println("Dog is barking");
}
public void eat()
{
System.out.println("Dog is eating");
}
}
Multi Level Inheritance
Single Child class extends parent class and parent class extends another super parent class is called Multi-Level Inheritance
As you can see Lion extends Cat and Cat extends Animal so Lion can inherit all the properties of Cat as well as Animal i.e., Multi-Level Inheritance
Cat Inherits Animal
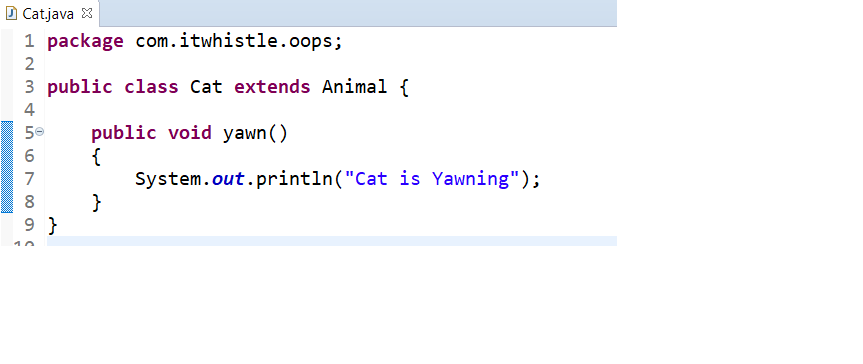
Lion Inherits Cat where as Cat Inherits Animal ie., Multi-Level Inheritance

package com.itwhistle.oops;
public class Cat extends Animal {
public void yawn()
{
System.out.println("Cat is Yawning");
}
}
package com.itwhistle.oops;
public class Lion extends Cat {
public static void main(String a[]) {
Lion lion = new Lion();
//Lion property
lion.roar();
//Lion inherits Cat property i.e., Yawn
lion.yawn();
//Lion inherits Animal property ie., sleep, drink and walk
lion.sleep();
lion.drink();
lion.walk();
}
public void roar() {
System.out.println("Lion is roaring");
}
}
Multiple Inheritance is not available in Java Inheritance. Single child class extends two super classes in just one class i.e., Multiple Inheritance
Multiple Inheritance is possible in Interface in java
Abstraction
Abstraction means user wont be able to see all the details of the class rather he would be able to see only relevant details
All Non relevant details will not be displayed to the user
Abstraction can be achieved using abstract class or an interface
Abstract Class

- abstract class can contain both abstract and non abstract methods
- It uses abstract keyword in front of the java class
- abstract methods usually wont contain the method body it will only contains the signature
- abstract class can not be instantiated, it can only inherited using extends keyword
- Either child class has to implement the abstract methods or the child class has to be abstract class too
ITWhistle() is an abstract method

In Eclipse you can always click on “Add Unimplemented methods”

In Eclipse you can always click on “Add Unimplemented methods”
You will see @Override for every implementation of abstract method by default

As a result, call both abstract and non abstract methods in child class

package com.itwhistle.oops;
public abstract class AbstractITWhistle {
public void callNonAbstract() {
System.out.println("Say hi to IT Whistle through non abstract");
}
public abstract void ITwhistle();
}
package com.itwhistle.oops;
public class TestITWhistle extends AbstractITWhistle {
@Override
public void ITwhistle() {
// you can have your own logic which will not viewable in abtract class
System.out.println("Implemented method of AbstractITWhistle ");
}
public static void main(String a[]) {
TestITWhistle obj = new TestITWhistle();
// calling implmented method in child class
obj.ITwhistle();
// calling parent class non abstract method
obj.callNonAbstract();
}
}
Encapsulation
Encapsulation hides the data into one single class. It is a process of wrapping code and data into single unit like a capsule which is mix of several medicines

You can accomplish encapsulation by
- Declaring private variables
- Public getter and setters to view or modify the values
In the below example you will see variables are declared private and getters/setters are declared public

Therefore, setting the age, name and grade and getting the values by calling the getter methods

package com.itwhistle.oops;
public class EncapsulationITWhistle {
private String name;
private String age;
private String grade;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getGrade() {
return grade;
}
public void setGrade(String grade) {
this.grade = grade;
}
}
package com.itwhistle.oops;
public class TestEncapITWhistle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EncapsulationITWhistle obj = new EncapsulationITWhistle();
obj.setAge("21");
obj.setName("It Whistle");
obj.setGrade("A");
System.out.println("Printing the student Name " + obj.getName());
System.out.println("Printing the student Age " + obj.getAge());
System.out.println("Printing the student Grade " + obj.getGrade());
}
}