Binary operators performs operations between two operands
Lets go through different types of Binary operations with java coding example below:
Addition
Adds two operands . The below code example adds two numbers x=1, y=2 and as a result z prints 3

package com.test.basics;
public class TestArthmeticOperator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int z;
int x=1;
int y=2;
z=x+y;
System.out.println("Adding two numbers "+z);
}
}
Likewise you can also use ‘+’ for string concatenation. The below example adds two string “Hello” and “World” and as a result it prints the concatenated value “HelloWorld”

package com.test.basics;
public class TestStringConcatenation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String con = "Hello" + "World";
System.out.println("Printing the concatenated value " + con);
}
}
Subtraction
It subtracts two operands. The below example subtracts two numbers x=10, y=5 and as a result z prints 5

package com.test.basics;
public class TestSubtraction {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int z;
int x = 10;
int y = 5;
z = x - y;
System.out.println("Subtracting two numbers " + z);
}
}
Multiplication
It multiplies two operands. The below example multiplies two numbers x=5, y=5 and as a result z prints 25.
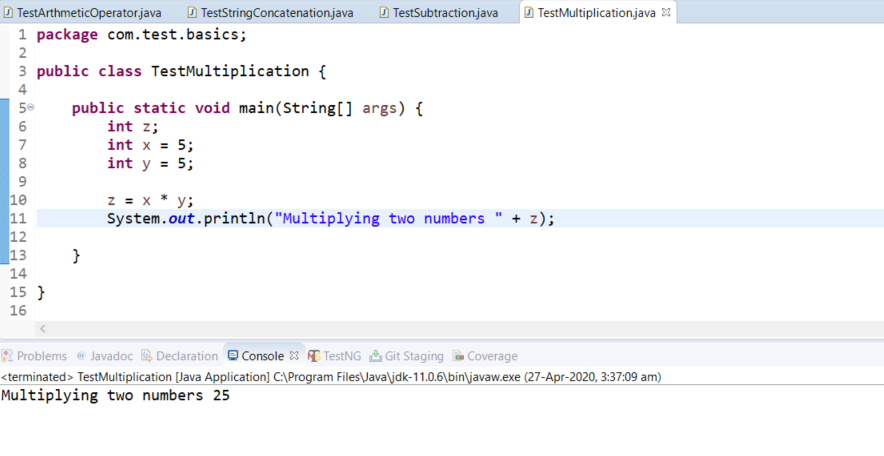
package com.test.basics;
public class TestMultiplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int z;
int x = 5;
int y = 5;
z = x * y;
System.out.println("Multiplying two numbers " + z);
}
}
Division
It divides first operand by second operand. The below example divides two numbers x=25, y=5 and as a result prints z=5

package com.test.basics;
public class TestDivision {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int z;
int x = 25;
int y = 5;
z = x / y;
System.out.println("Dividing first number by second " + z);
}
}
Modulus
First operand is divided by the second and returns the reminder. The below example divides first number x= 20 by second number y=6 and as a result it returns reminder 2.

package com.test.basics;
public class TestModulus {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int z;
int x = 20;
int y = 6;
z = x % y;
System.out.println("Reminder for first number divided by second number " + z);
}
}