Loops for Java
Loops allows you to execute group of statements multiple times.
There are different types of loops in java
- While loop
- do while loop
- For loop
- Switch Case
- For each
While Loop
It repeats a statement or group of statements while a given condition is true. It tests the condition first before executing the loop body.
Flow diagram:

Syntax:
while ( condition )
statement;Statement will get executed repeatedly until the condition becomes false
Example:
It executes the loop until the condition matches i =10 then the conditions becomes false for i=11 and it will stop loop execution

package com.itwhistle.loops;
public class TestITWhistleWhileLoop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
while (i <= 10) {
System.out.println("printing the value of i " + i);
i++;
}
}
}
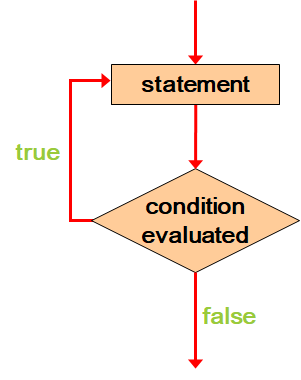
Do While Loop
The statement gets executed once initially and then the condition is evaluated.
The statement gets executed repeatedly until the condition becomes false
Flow Diagram:
Syntax:
do
{
statement;
}
while ( condition );Example:
The DO While loop executes first then evaluates condition i<=10, it will print 11 then the loop stops because it executes the statement first!

package com.itwhistle.loops;
public class TestITWhistleDOWhileLoop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
do
{
i++;
System.out.println (i);
} while (i <=10);
}
}
For Loop
A for loop is equivalent to while loop when you use the following while structure
initialization;
while ( condition )
{
statement;
increment;
}In a for loop you can initialize a variable, write a condition and increment in just one line.
It is similar to while loop where condition is evaluated before executing a for loop
So the for loop will execute 0 or more times
Flow Diagram:

Syntax:
for ( initialization ; condition ; increment )
statement;- initialization is executed once before the loop begins
- condition is evaluated before loop runs
- it increments at the end of every iteration
Example:
It initialize i=0, evaluates condition is less than or equal to 10 and increments the i
Loop will run until the condition is true i.e., i<=10 when condition is false i.e., i=11 it breaks the loop.
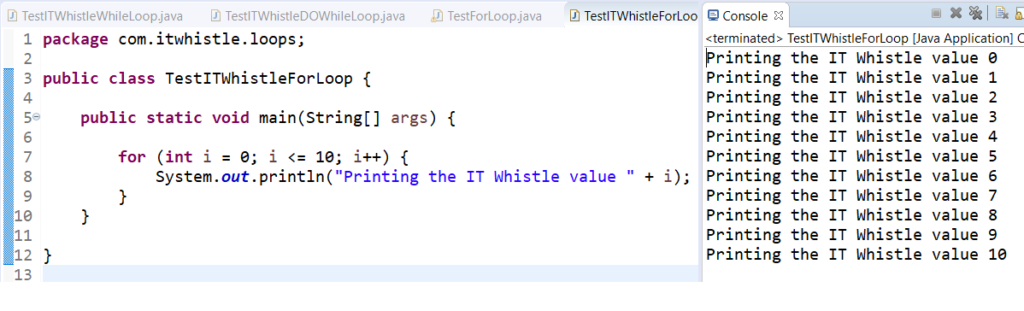
package com.itwhistle.loops;
public class TestITWhistleForLoop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i++) {
System.out.println("Printing the IT Whistle value " + i);
}
}
}For Each loop:
For each loop is also called as Enhanced for loop. It mainly uses to traverse collection of elements or arrays
Syntax:
For(declaration: expression){
//Statement or Group of Statements
}declaration- The newly declared block variable, is of a type compatible with the elements of the array you are accessing. The variable will be available within the for block and its value would be the same as the current array element.
expression- It evaluates the array you loop through. The expression can be an array variable or method call that returns an array.
Example:
In the below example, for each loop will run until it loop through the array i.e., till three

package com.itwhistle.loops;
public class TestITWhistleForEachLoop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a[]= {"one","two","three"};
for (String value: a) {
System.out.println("Printing the IT Whistle value " + value);
}
}
}